5 Essential Tips for Converting Beer Recipes Easily
In the world of homebrewing, the ability to convert beer recipes is not just a skill, it's an art form. It allows you to adapt recipes to suit different batch sizes, brewing methods, or even experiment with different ingredients. This blog post will delve into five essential tips that every homebrewer should know when converting beer recipes, ensuring you achieve the desired results every time.
Understanding Beer Recipe Ratios


Before you start converting recipes, it’s crucial to understand the basic ratios in brewing:
- Fermentable ingredients like malt, which form the backbone of your beer’s body and flavor.
- Hops for bitterness, flavor, and aroma.
- Water, which should be adjusted for the recipe’s chemistry needs.
- Yeast, the life force that ferments your beer.
🔍 Note: Understanding these ratios will help you scale your recipes accurately.
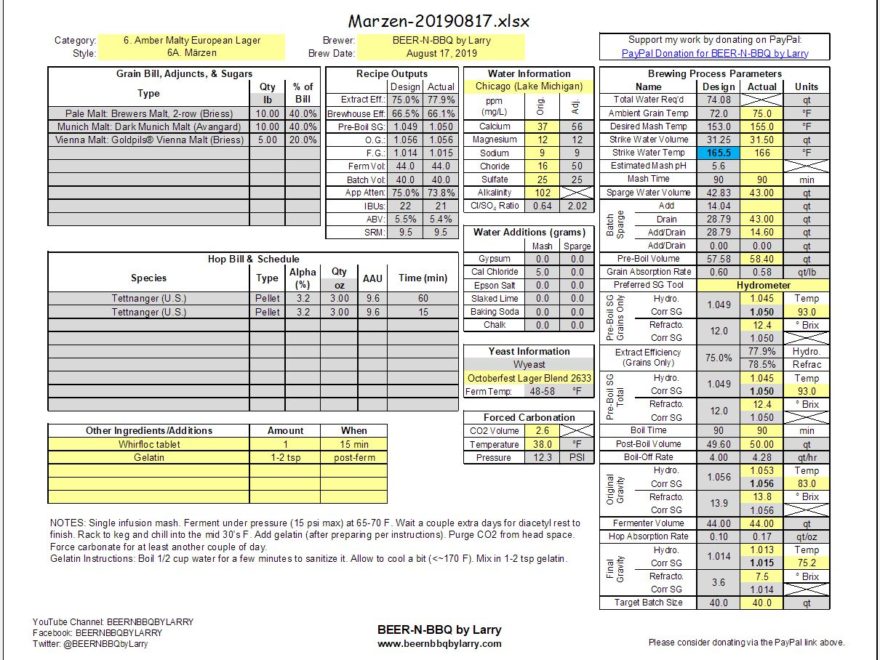
Tip 1: Scaling Ingredients Proportionally

When converting a recipe, the most straightforward approach is to scale all ingredients proportionally. Here’s how you can do it:
- Determine the volume ratio of your new batch size to the original batch size.
- Multiply each ingredient by this ratio to find the new quantities. For example, if you’re scaling up from 5 gallons to 10 gallons, use a ratio of 2:1.
| Original Recipe | Converted Recipe |
|---|---|
| 5 lbs of malt | 10 lbs of malt |
| 1 oz of hops | 2 oz of hops |

📝 Note: Not all ingredients scale linearly. Hops, in particular, can require some adjustments based on the desired IBU (International Bitterness Units).
Tip 2: Adjusting for Boil Gravity

Changes in batch size can affect the boil gravity, which influences:
- The efficiency of hop extraction
- Extract yield from grains
- Overall fermentation behavior
Here’s what you need to consider:
- If you’re scaling up, increase the amount of water to achieve the same boil gravity.
- For smaller batches, reduce the water to maintain the same extraction efficiency.
📊 Note: This tip ensures your beer maintains its intended flavor profile despite the change in volume.
Tip 3: Hop Utilization and Bitterness

Hops play a vital role in beer’s bitterness and flavor, and their utilization can change with the batch size:
- Larger batches: Hops contribute less bitterness due to lower boil gravity.
- Smaller batches: Higher boil gravity might require less hops to achieve the same bitterness.
Consider using a hop utilization calculator or formula like Tinseth or Rager to adjust hop additions accurately:
IBU = [Hops in grams x % Alpha Acid x Utilization Factor] / [Batch Volume in Liters x 10]
🏗️ Note: This step helps in maintaining the balance of flavor, especially in beers where hops are a prominent feature.
Tip 4: Yeast Pitch Rates

Yeast quantity needs to match the amount of fermentables to ensure optimal fermentation. Here’s how to adjust:
- Use a yeast pitching calculator to determine the appropriate cell count for your batch size.
- Remember, scaling a recipe by volume doesn’t always mean scaling yeast by the same proportion due to changes in wort composition.
🔬 Note: This adjustment is crucial for consistent fermentation profiles across different batch sizes.
Tip 5: Monitoring and Adjusting Fermentation

The fermentation stage can be significantly affected when you change the batch size:
- Check fermentation temperature, which might need adjustment to control yeast activity.
- Monitor specific gravity readings to ensure fermentation is progressing as expected.
Ensure that:
- You have adequate fermentation vessel space for the increased volume.
- Yeast nutrients are scaled accordingly, especially in larger batches where nutrients can become diluted.
⚗️ Note: Proper fermentation management ensures your beer has the desired flavor and alcohol content.
By following these five tips, you're well on your way to becoming adept at converting beer recipes. The key is to understand the nuances of brewing, including how different ingredients interact and how batch size affects your beer's final profile. Remember, brewing is both a science and an art, where precision meets creativity.
Why does changing batch size affect hop utilization?

+
When you change the batch size, the boil gravity changes, which impacts how well hops are utilized for bitterness and flavor extraction during boiling.
How can I accurately measure the specific gravity for different batch sizes?
+
Use a hydrometer or refractometer, adjusting the volume of the sample to reflect the batch size for accurate readings. Compensate for temperature variations as well.
What are the common issues when scaling up beer recipes?

+
Common issues include insufficient fermentation space, altered boil dynamics affecting hop utilization, and potential inconsistencies in fermentation due to different yeast pitch rates.